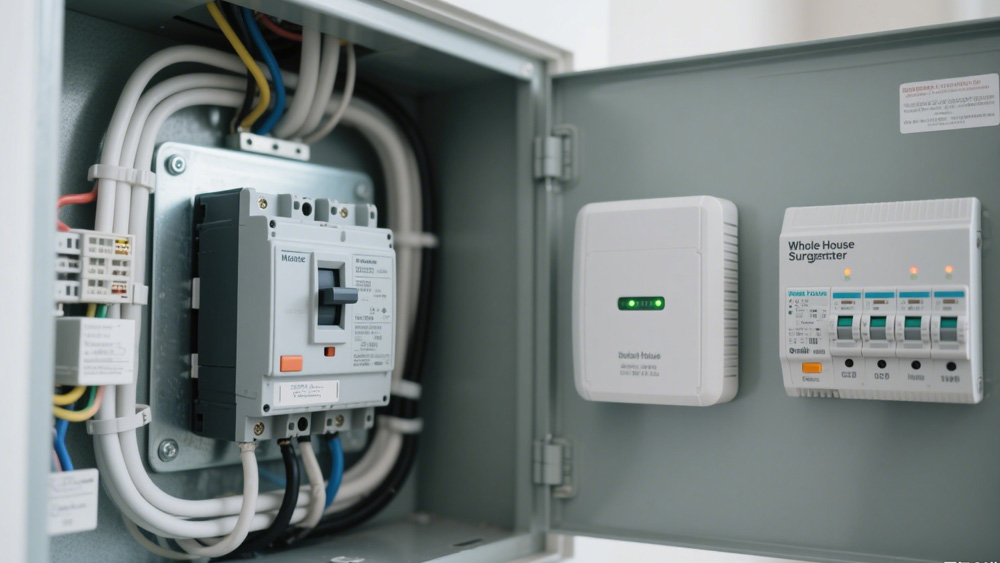
Electrical safety is one of the most critical considerations for any home or business. Two terms that often come up are circuit breakers and surge protectors. At first glance, they may seem to do the same thing—protect your electrical system—but in reality, they address very different risks.
If you have ever wondered, “Is a whole house surge protector worth it?” or “Do I need a circuit breaker with a surge protector?” We’ll explore the differences between a surge protector and a circuit breaker, their pros and cons, and how to choose the right protection for your needs.
What Is a Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is a core component of any modern electrical system. Its primary role is to protect your home’s wiring and prevent dangerous situations like overheating and fires.
Circuit breakers provide overload protection by cutting power when too many appliances are plugged in. They also provide short-circuit protection, tripping immediately if two wires touch in a way that could spark or cause fire. Another advantage is that they are resettable, unlike fuses which must be replaced after blowing.
Installed in the main electrical panel, circuit breakers are mandatory in residential and commercial properties because they serve as the first line of defense against electrical hazards. However, a circuit breaker surge protection system does not automatically guard against voltage spikes. This is a common misconception. A breaker responds to current overload, not to sudden surges caused by lightning or utility grid issues.
What Is a Surge Protector?
A surge protector, on the other hand, is specifically designed to safeguard your electronics and appliances from sudden increases in voltage.
Main Functions of a Surge Protector
- Voltage spike protection: Redirects excess electricity safely to the ground.
- Equipment shielding: Protects sensitive devices like TVs, computers, and smart home appliances.
- Whole-home safety: A whole-house surge protector can be installed at the main panel to protect every outlet in your home.
Surges may come from lightning strikes, downed power lines, or even your own large appliances turning on and off. Without a surge protector, these spikes can shorten the lifespan of your electronics or even destroy them instantly.
A whole-house surge protector can make a significant difference, especially if you live in storm-prone regions or rely heavily on expensive electronics.
Main Differences Between a Circuit Breaker and a Surge Protector
Circuit Breakers vs. Surge Protectors
| Feature | Circuit Breaker | Surge Protector |
| Primary Function | Protects against overcurrent (overloads and short circuits) | Protects against overvoltage (spikes and surges) |
| Goal | Prevents fire hazards | Prevents electronic damage |
| Installation | Typically, in breaker panels | Plug-in strips or panel-mounted devices |
| Response | Trips when the current exceeds a safe level | Redirects excess voltage instantly |
| Limitations | Does not block surges | Does not stop fires |
In practical terms, a circuit breaker keeps your home safe from electrical fires caused by too much current, while a surge protector shields your electronics from sudden voltage spikes.


