Get quick appointment for technical support!
Understanding the 16-Amp Fuse: A Comprehensive Guide for Home and Industrial Use
Sep 26, 2025
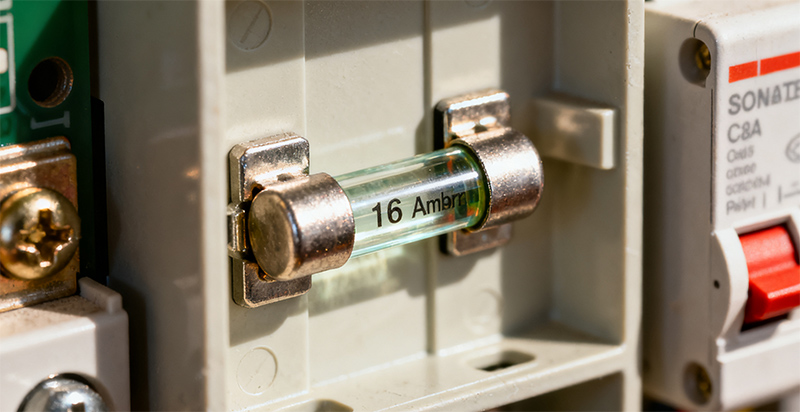

A 16-amp fuse may seem like a small component in your home or industrial electrical system, but it plays an important role in ensuring safety and efficiency.
From household appliances to industrial machinery, understanding the specifications and proper usage of a 16 amp fuse can prevent accidents, protect equipment, and improve the overall performance of your electrical setup. In this guide, we will explore everything you need to know about 16-amp fuses, including their characteristics, types, and best practices for installation and replacement.
Understanding the “16 Amps” Rating
Maximum Current Capacity
The designation “16 amps” refers to the maximum current the fuse can safely carry before blowing or interrupting the circuit. Understanding this rating is important for correctly sizing breakers and panel wire, preventing overcurrent situations that could lead to damage or fire.
Practical Applications and Voltage Rating
In practical terms, the 16 ampere-watt rating provides a clear indication of the fuse’s capacity when paired with the system voltage. For instance, a 16 amp 250V fuse is commonly used in residential and industrial circuits where reliable protection is needed under these voltage and current conditions.
Energy Handling and Compatibility
Additionally, the 16 ampere in watts measurement allows users to calculate the energy handling capability of the fuse. This ensures that the fuse is compatible with connected devices, accommodates temporary current spikes, and maintains consistent protection, giving both safety and performance benefits in various electrical setups.
Different Types of Fuses
16 amp fuses come in various forms to cater to different applications. Some common types include:
Cartridge Fuses
Commonly used in household appliances and industrial machines, cartridge fuses offer reliable protection and easy replacement. These fuses are robust and can handle moderate inrush currents, making them suitable for many electrical devices. Their replaceable nature ensures minimal downtime in both residential and industrial settings.
Glass Tube Fuses
Often found in smaller electronic devices, these fuses provide visual confirmation of a blown fuse. They are lightweight, easy to install, and ideal for circuits where space is limited. Additionally, glass tube fuses offer fast response times to protect sensitive electronics.
Ceramic Fuses
Designed to handle higher temperatures and inrush current, ceramic fuses are durable and ideal for demanding environments. They can withstand power surges and maintain integrity over repeated thermal cycles, making them suitable for high-load appliances and industrial machinery.
Blade Fuses
Common in automotive applications, blade fuses are compact, standardized, and simple to replace. They are color-coded for easy identification and are designed to withstand vibrations and temperature variations typical in vehicle environments.
Each type of fuse serves a specific purpose, and choosing the right one depends on the current rating, voltage, inrush current, and intended application. Proper selection ensures optimal protection, longevity, and safety for any electrical system.
Understanding the Key Differences Between Fuses and Circuit Breakers
While both fuses and circuit breakers are designed to protect electrical systems, their operation and functionality differ significantly.
How a Fuse Operates
A fuse contains a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows, effectively breaking the circuit. This single-use mechanism ensures that the overcurrent does not reach sensitive devices or wiring.
How a Circuit Breaker Operates
In contrast, a circuit breaker uses a mechanical switch that trips when an overcurrent is detected. Once the issue is resolved, the circuit can be reset without replacing any components, making it reusable and convenient for frequent overcurrent events.
Selecting the Right Protection Device
Understanding these differences is essential for sizing breakers and selecting complementary protection devices alongside 16 amp fuses. Fuses provide fast-acting protection, whereas circuit breakers offer flexibility and reusability depending on the application.
What is a Switch Fuse Unit?
A switch fuse unit combines a switch and a fuse into a single device, allowing both manual control and overcurrent protection. This setup is particularly useful in industrial environments where equipment needs to be isolated safely for maintenance or emergency situations.
A switch fuse unit simplifies the installation process, reduces wiring complexity, and ensures that the 16 amp fuse operates efficiently within its specified range.
How Does a Fuse Work?
A fuse functions as a sacrificial device designed to protect electrical circuits from overcurrent.
Fuse Mechanics and Heat Response
When current exceeds the rated 16 amps, the fuse element heats up and melts, interrupting the flow of electricity. The design of the fuse ensures rapid response to sustained overcurrent while tolerating brief inrush current spikes.
Protection Against Damage
This interruption prevents overheating, fire hazards, and damage to connected equipment, acting as a first line of defense in electrical safety.
Consideration of Inrush Current
Factors such as inrush current—temporary spikes in current when devices start—must be carefully considered when selecting a fuse to avoid unnecessary blowing during normal operation. Selecting the right type and rating ensures that the fuse only acts under true overcurrent conditions, maintaining system reliability.
Choosing the Correct Size and Quality of Fuse
Selecting the appropriate fuse size and quality is important for maintaining electrical safety. Using an incorrect 16 amp fuse can result in equipment damage, overheating, or even fire. High-quality fuses provide consistent performance, dependable protection, and long service life.
Proper selection also requires assessing panel wire capacity, voltage rating (such as 16 amp 250V fuse), and the nature of the connected load to ensure compatibility and adherence to safety standards.
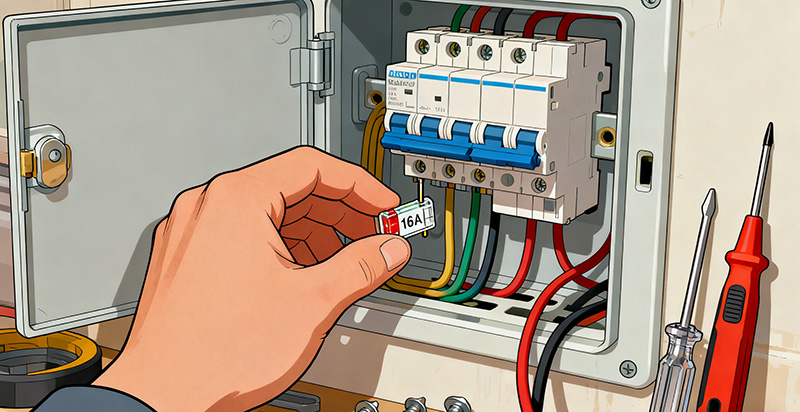
How to Safely Replace a Fuse in an Old Fuse Box
Replacing a fuse in an old fuse box can be straightforward if proper precautions are followed. Having the correct replacement fuse and understanding the steps beforehand can make the process safer and more efficient.
Step 1: Turn Off Power
Replacing a fuse requires careful attention to safety. First, turn off the main power supply to prevent electric shock. Inform others in the household that the power is off, and use a flashlight if necessary.
Step 2: Remove and Inspect the Fuse
Remove the blown fuse and carefully inspect it to confirm the type, rating, and any visible damage. Typically marked as 16 amp or similar, this check ensures the replacement matches the circuit requirements. Inspect the fuse holder for corrosion or signs of overheating.
Step 3: Insert the New Fuse
Insert a new fuse of the same rating, making sure it fits securely in the holder. Ensure the fuse is properly seated to prevent loose contacts, arcing, or uneven current flow. Double-check that the surrounding wiring is intact and undamaged.
Step 4: Restore Power and Test
After installation, restore power and test the circuit to confirm correct operation. Monitor the circuit for unusual behaviour, flickering, or tripping. Using this careful approach helps maintain safety and reliability during the fuse replacement process.
Conclusion
A 16-amp fuse is more than just a protective device; it is a vital component in ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. From understanding its current and watt ratings to choosing the right type, quality, and installation method, knowledge of 16-amp fuses empowers both homeowners and professionals to maintain reliable and safe electrical operations.
Proper sizing of breakers, attention to panel wire compatibility, and consideration of inrush current are all critical elements that contribute to the overall effectiveness of a 16-amp fuse in any application.
--- END ---
In this blog
Featured Articles
Get A Free Quote

