Get quick appointment for technical support!
Voltmeter Measures: A Guide to Voltage
Aug 25, 2025
When it comes to understanding electricity, one of the fundamental tools you’ll encounter is the voltmeter. While it may seem simple, the voltmeter is essential for both learning and professional work with electronics.
This guide aims to explain what a voltmeter measures, how it works, the different types available, and how it supports both basic learning and advanced applications in electrical testing.
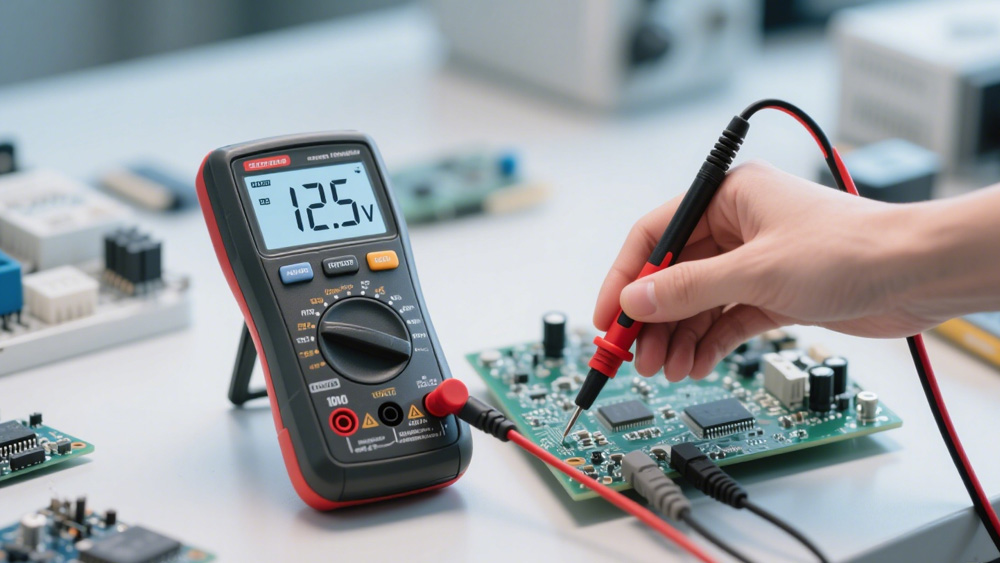
What is a Voltmeter?
A voltmeter is an instrument used to measure the electrical potential difference, commonly known as voltage, between two points in a circuit. Put simply, a voltmeter measures voltage between two points in a circuit.
Its purpose is to provide reliable readings of how much electrical force is moving current through a circuit, helping ensure that devices and systems operate within safe ranges. Voltmeters display results in volts (V), the standard unit of voltage, making it easy to evaluate electrical performance.
The Basics of How Voltmeters Work
A voltmeter is connected in parallel with the component or section of a circuit under test. By being connected this way, the voltmeter can detect the potential difference across two points without significantly affecting the circuit’s operation.
- Volt measurement principle: The voltmeter works by comparing the electrical potential between two points and displaying the difference as a numeric value.
- Voltmeter symbols: On circuit diagrams, a voltmeter is represented by a circle with the letter V. This symbol makes it easy to identify where voltage readings are taken.
- A voltmeter is used to measure: Voltage between the terminals of batteries, across resistors, or at power outlets.
If you’ve ever wondered “how to read the voltmeter,” the process is simple. First, select the correct range on the device (AC or DC, depending on the circuit). Then, place the probes across the two points you want to test. The digital or analogue display will show the voltage value, which is the voltage measured at that point.
What are the Types of Voltmeters?
Over time, voltmeters have evolved to meet the growing complexity of electrical systems. The most common types include:
1. Analogue Voltmeters
Analog voltmeters use a moving needle to show the voltage on a dial. They provide continuous readings and are still popular in laboratories and training environments for demonstrating how voltage fluctuates.
2. Digital Voltmeters
Digital models display readings on an LCD or LED screen. They are more precise and easier to read, especially for beginners.
3. Portable Handheld Voltmeters
These are common in fieldwork. Electricians use them for quick voltage checks in residential, commercial, or industrial settings.
4. Panel-Mounted Voltmeters
Found in control panels and monitoring systems, these voltmeters are installed permanently to provide continuous readings of system voltage.
Digital Voltmeters and Their Advantages
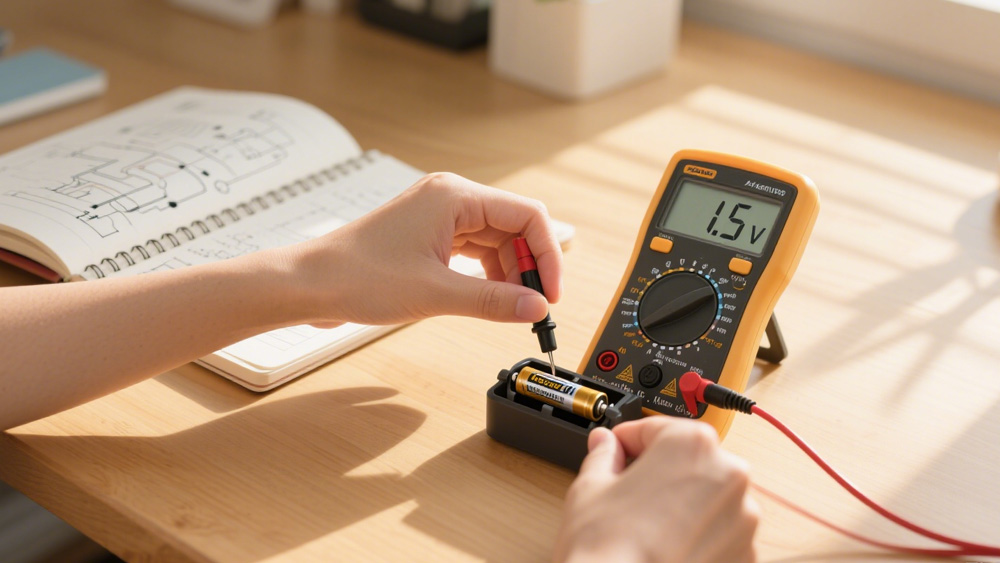

Among the various types, digital voltmeters have become the most widely used because they combine accuracy with convenience. Instead of a moving needle, they show voltage as a clear number on a screen, which makes the process simple for beginners and efficient for professionals.
Accuracy
A digital display reduces errors and provides precise measurements, often down to a fraction of a volt. This precision is valuable for both technical work and educational settings where small differences matter.
Usability
Many models adjust the range automatically, removing guesswork and making the process faster for users of all levels. Clear readouts also minimize confusion, which is especially helpful for learners.
Safety and Features
Advanced versions include features such as overload alerts, data hold functions, or even connectivity to computers and mobile devices. These additions enhance protection during use and allow results to be stored, shared, or analyzed more effectively.
Because of these combined advantages, digital voltmeters are now standard tools in electrical work, laboratories, and classrooms. They make volt measurement accessible, reliable, and efficient, even for those just starting out.
Common Application Scenarios of Voltmeters
Voltmeters are widely used in daily life and professional settings. They help test batteries, check outlets at home, monitor voltage in industrial systems, support education and training, and assist in troubleshooting electronics. In every case, the principle is the same: the voltmeter measures the potential difference between two points, providing useful insights into system performance.
Conclusion
A voltmeter is an important tool for anyone working with electricity. It helps ensure safety, accuracy, and efficiency in electrical systems. Knowing how to read the voltmeter and understanding its applications allows both professionals and beginners to use it with confidence.
By mastering volt measurement and recognizing voltmeter symbols, you can handle everything from simple home projects to complex industrial systems. The voltmeter remains a reliable companion in understanding and managing electrical energy.
--- END ---
In this blog
Featured Articles
Get A Free Quote

